
อวัยวะต่าง ๆ ที่รับความรู้สึกพิเศษมี sensory receptors ซึ่งเป็นฐานประสาทรับความรู้สึกพิเศษ (specific neuralreceptors) โดยร่วมทำงานกับโครงสร้างที่ไม่ใช่เนื้อประสาท เพื่อเพิ่มขีดความสามารถให้เป็นฐานรับความรู้สึกที่ละเอียดอ่อนต่อสิ่งที่มากระตุ้นอวัยวะที่รับความรู้สึกพิเศษ ได้แก่ ตาและหู (audio-vestibular apparatus)ซึ่งเป็นอวัยวะสำคัญของระบบนี้ รวมทั้งฐานประสาทรับรสและกลิ่น นับรวมอยู่ในระบบนี้เช่นกันนอกจากนั้นยังรวมทั้ง organs of general sensibility หรือ Sensory nerve endingsซึ่งทำหน้าที่รับความรู้สึกต่าง ๆ ตามร่างกายทั่วไป บางชนิดมีเนื้อประสานมาห่อหุ้มอวัยวะดังกล่าวได้แก่ free nerve endings และ encapsulated nerve endings (ได้แก่ Meisser'scorpuscle, Pacinian corpuscle, End-bulb of Krause, Corpuscle of Ruffiniและ Neuromuscular spindles ตามลำดับ)
ระบบการรับความรู้สึกประกอบด้วยอวัยวะ 5พวก คือ
I. EYE (ตา) เป็น sensory organ ที่มีเลนส์ทำหน้าที่โฟกัสลำแสงจากภายนอกให้ไปตกที่จอภาพretina ซึ่งประกอบด้วย photosensitive cells ลูกตามีเปลือกตา (eyelids) ปกป้องลูกตาผิวด้านหน้าของลูกตามีน้ำตา (tear) หล่อเลี้ยงตลอดเวลา น้ำตาสร้างมาจาก lacrimalglands ผนังของลูกตาแบ่งออกเป็น 3 ชั้นคือ outer fibrous tunic, middle vasculartunic (uvea) และ inner (photosensitive) retinal tunic ดังนั้นหน้าที่ของตาคือรับภาพและแสง
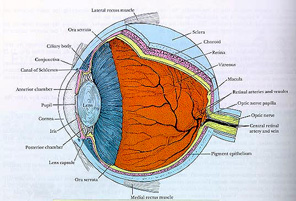 | ต่อจากนี้ศึกษาภาพวาด แสดงโครงสร้างภายในลูกตาจาก Histology : A Text and Atlas, 3rd ed., by Ross et al., Chapter 23,pp. 742, 1995 |
A. Fibrous Tunic (corneoscleral layer)ประกอบด้วย 2 ส่วน1. Cornea (แก้วตา) (Figure175) อยู่ด้านหน้า ใส มี 5 ชั้นa. Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
b. Bowman's membrane
c. Stroma
d. Descemet's membrane (thick basal lamina)
e. Corneal endothelium (not a true endothelium)
2. Sclera บริเวณที่เชื่อมต่อกับ corneaเรียก limbus ลักษณะของ sclera เป็นผนังสีขาวอยู่ทางด้านหลัง มี 3 ชั้น แยกออกจากกันได้ยากได้แก่ outer episcleral tissue (มีหลอดเลือดและเนื้อประสานชนิดหลวม), middlestroma หรือ Tenon's capsule (dense regular collagenous connective tissue)และ suprachoroid lamina หรือ lamina fusca (เนื้อประสานชนิดหลวมบรรจุ fibroblastsและ melanocytes) ชั้น sclera มีหลอดเลือด เส้นประสาท และ optic nerve ผ่านทะลุ
B. Vascular Tunica (uvea) เป็นชั้นที่นำอาหารไปเลี้ยงจอภาพretina โดยประกอบด้วย 3 บริเวณคือ choroid membrane, ciliary body และ iris1. Choroid membrane (Figure174) ประกอบด้วย 4 ชั้น คือ1.1 suprachoroid layer ร่วมติดอยู่กับ scleraบรรจุ fibroblasts และ melanocytes
1.2 vascular และ choriocapillary layers บรรจุหลอดเลือดดำ-แดงหลายขนาดและหลอดเลือดฝอย
1.3 glassy membrane (of Bruch) ติดอยู่กับretina ซึ่งให้เป็น basal lamina
2. Ciliary body (Figure172 A, B) อยู่ระหว่าง ora serrata (ขอบเขตที่ retina บางและเริ่มไม่มีreceptor cells) และ iris โครงสร้างนี้ประกอบด้วย ciliary process (สร้างaqueous humor) และส่วนที่ยึดกับ suspensory ligament (เส้นใยยึดเลนส์ตามี2 ข้าง) เรียก ciliary crown ใน ciliary body บรรจุกล้ามเนื้อเรียบ 3 ชั้นทำหน้าที่เกี่ยวกับ accommodation ของลูกตา ชั้น vascular และ glassy membraneของ choroid ต่อเนื่องมาคลุมบน ciliary body ด้านในสุดของ ciliary body คลุมด้วยinner nonpigmented และ outer pigmented layers ของ ciliary epithelium
3. Iris (Figure172 A, B) เป็นโครงสร้างที่กั้น anterior chamber ออกจาก posterior chamberและยึดติดกับ ciliary body บริเวณศูนย์กลางของ iris คือ pupil ของลูกตา irisทำหน้าที่เป็น contractile diaphragmIris ประกอบด้วยชั้น 3 ชั้น
3.1 outer simple squamous epithelium layerต่อเนื่องกับ corneal epithelium
3.2 middle fibrous layer ประกอบด้วย nonvascularanterior stromal และ vascular general stromal layer
3.3 posterior pigmented epithelium (membrame)เป็นชั้นทบของ pigmented epithelial cells และพบ sphincter pupillae และ dilatorpupillae muscles ของ pupils ซึ่งประกอบด้วย myoepithelial cells (กำเนิดมาจากpigmented epithelium)
C. Retinal Tunica (Figure173), (174) เป็นชั้นลึกสุดติดกับ vitreousbody ประกอบด้วย 3 บริเวณคือ pars iridica, pars ciliaris และ pars opticaโดยส่วนสุดท้ายเป็นบริเวณที่ไวต่อแสง1. Pars Optica (Figure174) ประกอบด้วยชั้น 10 ชั้น(10) a. Pigment Epithelium ติดกับchoroid membrane
( 9) b. Lamina of Rods and Cones บรรจุphotoreceptor cells ซึ่งมี 2 ชนิด คือ rhodopsin - synthesizing rods (ไวต่อแสงสลัว)และ iodopsin-forming cones (ไวต่อแสงจ้า)
( 8) c. External Limiting membraneเป็นชั้น junctional specialization ระหว่าง photoreceptor cells และแขนงของMuller's (supportive) cells
( 7) d. Outer Nuclear Layer บรรจุcell bodies (และนิวเคลียส) ของ photoreceptor cells แต่ตรงบริเวณ fovea centralisมีแต่ cones
( 6) e. Outer Plexiform Layer บริเวณsynapse ระหว่าง axons ของ photoreceptor cells และแขนงของ bipolar และ horizontalcells
( 5) f. Inner Nuclear Layer บรรจุcell bodies ของ Muller, amacrine (associative), bipolar และ horizontalcells
( 4) g. Inner Plexiform Layer บริเวณsynapses ระหว่าง dendrites ของ ganglion cells และ axons ของ bipolar cellsนอกจากนั้นยังพบแขนงของ Muller และ amarine cells
( 3) h. Ganglion cell Layer บรรจุcell bodies ของ multipolar neurons และ axons รวมให้เป็น optic nerve นอกจากนั้นยังพบneuroglia
( 2) i. Optic Nerve Fiber Layer ประกอบด้วยunmyelinated axons ของ ganglion cells ซึ่งรวมให้เป็น optic nerve (Figure173) ออกจากลูกตาไป synapse ในสมอง
(1) j. Inner Limiting membrane ประกอบด้วยแขนงปลายที่แผ่ออกของMuller cells
2. Pars Ciliaris และ Pars Iridica Retinaบริเวณนี้ชั้น retina บาง คงเหลือแต่ epithelial layer ซึ่งประกอบด้วย columnarและ pigmented layer ชั้นเดียว ดาด ciliary body และ iris
D. Lens (Figure172 A) เป็น biconvex ยืดหยุ่น ใส ไม่มีหลอดเลือด และยึดกับส่วนบนของciliary body ด้วย zonule หรือ suspensory ligament ทำหน้าที่โฟกัสลำแสงให้ไปตกที่จอภาพretina ประกอบด้วย 3 ชั้น1. elastic capsule (basement membrane)หนา 10-20 ไมโครเมตร สร้าง lens cells ทางด้านหนา
2. simple cuboidal epithelium หรือsubcapsular epithelium พบอยู่ทางด้านหน้าเท่านั้น
3. lens fibers เจริญมาจาก subcapsularepithelial cells ตรงบริเวณ equator ของ lens ต่อมาเพิ่มส่วนสูง และเปลี่ยนเป็นเส้นใยเลนส์
E. Lacrimal gland (ต่อมน้ำตา) พบบริเวณsuperolateral aspect ของกระบอกตาเป็น compound tubuloalveolar gland สร้างและหลั่งlysozyme-rich serous fluid มี ph เป็นด่าง
F. Eyelid (เปลือกตา) คลุมด้านบนด้วยผิวหนังชนิดบางด้านในเป็น conjunctiva (mucous membrane) แกนกลางเป็น tarsal plate (densefibrous connective ที่หนา) พบ tarsal glands สร้างและหลั่งไขมัน มีกล้ามเนื้อลาย2 มัดในเปลือกตา คือ orbicularis oculi และ levator palpebrae superiorisต่อมไขมันสัมพันธ์อยู่กับ eyelashes (ขนตา)
| II. EAR (หู) มีหน้าที่รับเสียงและเกี่ยวกับการทรงตัวของศีรษะจากภาพวาด แสดงโครงสร้างหูซึ่งแบ่งออกเป็น 3 ส่วน คือ external ear (ใบหู),middle ear (tympanic cavity, ossicles, tympanic membrane และ auditory tube)และ inner ear (semicircular canals และ cochlea) (จาก Histology : A Textand Atlas, 3 rd ed., by Ross et al., Chapter 24, pp.769.) | 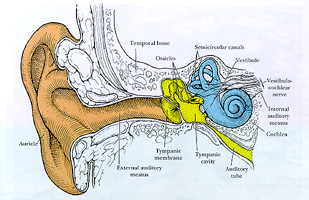 |
A. External Ear (หูด้านนอก) ประกอบด้วย1. Auricle (ใบหู) คลุมด้วยผิวหนังชนิดบางมีแกนกลางเป็น elastic cartilage plate
2. External Auditory meatus คือ ท่อที่มีผนังเป็นกระดูกอ่อนดาดด้วยผิวหนัง บรรจุ ceruminous glands และขนชนิดอ่อนบางเล็กน้อย ผนังตรงกลางท่อมีกระดูกแข็งเข้าไปแทนที่กระดูกอ่อน
3. Tympanic membrane (แก้วหู) บางเป็นตัวกั้นระหว่างหูส่วนนอกกับหูส่วนกลาง ดาดผิวด้านนอกด้วย stratified squamouskeratinized epithelium ผิวด้านในดาดด้วย low cuboidal epithelium แกนแก้วหูเป็นcollagen fibers
B. Middle Ear (หูส่วนกลาง) ดาดด้วย simplecuboidal epithelium บรรจุกระดูกแข็งที่เชื่อมต่อกัน 3 แท่ง คือ malleus,incus และ stapes หูส่วนนี้มีทางติดต่อกับnasopharynx ทางท่อที่ผนังเป็นกระดูกอ่อนและกระดูกแข็งคือ auditory tube ผนังด้าน medial ติดต่อกับหูส่วนในทาง oval (vestibular)และ round (cochlear) windows
C. Inner Ear (หูส่วนใน) มีหน้าที่เกี่ยวกับการได้ยินและการทรงตัวประกอบด้วย 2 labyrinthine compartments โดยมี 1 ช่องสวมอยู่ข้างในของอีกช่องได้แก่1. Bony (osseous) labyrinth ประกอบด้วย3 ช่อง และอยู่ใน temporal bone ได้แก่a. Semicircular canals เป็นท่อ 3 อันตั้งเป็นมุมฉากต่อกัน บริเวณด้านข้างของแต่ละ semicircular canal ที่เชื่อมต่อกับvesibule นั้น จะพองออกเป็น ampulla
b. Cochlea ยื่นออกทางด้านหน้าของ vestibuleลักษณะเหมือนหอยโข่ง มีแกนเรียก modiolus ซึ่งมีแผ่นกระดูกยื่นเข้าไปในท่อเรียกส่วนที่ยื่นว่า Osseous spiral lamina พบ spiral ganglion อยู่ใน modiolus
2. Membranous Labyrinth สวมอยู่ภายใน bonylabyrinth ประกอบด้วย ช่องย่อย 3 ช่อง คือa. Membranous semicircular ducts มี3 อันอยู่ใน semicircular canals ที่เป็นกระดูกแข็ง ปลายทั้ง 3 ของ ductsเปิดร่วมเข้าสู่กระเปาะที่เรียกว่า utricle
b. Utricle และ saccule บรรจุอยู่ในrecesses ของ vestibule และต่อเนื่องกันด้วย membranous utriculosaccularduct และ endolymphatic sac
c. Membranous cochlea (cochlear duct)อยู่ใน bony cochlea และต่อเนื่องกับ saccule
ของเหลวที่บรรจุในช่องหูส่วนใน ได้แก่- Endolymph อยู่ใน membranous labyrinth
- Perilymph อยู่ระหว่างผนังของ bonylabyrinth และ membranous labyrinth
- Cortilymph อยู่ภายใน organ of Corti
เซลล์ชนิดพิเศษที่เป็นฐานรับเสียงและการทรงตัวพบที่หูส่วนในมี 6 บริเวณ คือ- Cristae ampullaris (Figure176 B) มี 3 บริเวณอยู่ใน ampullae ของ semicircular ducts พวก neuroepitheliumบริเวณนี้มีความไวต่อการหันศีรษะ
- Maculae (Figure176 A) มี 2 บริเวณ คืออยู่ใน utricle เรียก macula utriculi และ อยู่ในsaccule เรียก macula sacculi พวก neuroepithelium ทั้งสองบริเวณไวต่อตำแหน่งของศีรษะและเคลื่อนศีรษะตามแนวราบ (linear)
- Organ of corti (Figure177) พบใน cochlear duct และยื่นเข้าไปอยู่ใน endolymph พวก neuroepitheliumเป็นฐานรับเสียง
III. Gustatory organs หรือ Taste budsพบอยู่ที่ผิวบนของลิ้น ทำหน้าที่รับรส (ศึกษาได้ในบทที่5) : (Figure 65, 67,68)IV. Organ of smell หรือ Olfactory epithelium(Figure171) พบที่ผนังของช่องจมูก ทำหน้าที่รับกลิ่น
V. Organs of general sensibility หรือ Sensorynerve endings ทำหน้าที่รับความรู้สึกต่างๆ ทั่วร่างกาย นั่นคือ กระจายอยู่ตามเนื้อผิวเนื้อประสาน และเนื้อกล้าม โดยปลายประสาทรับความรู้สึกจำแนกตามลักษณะได้เป็น2 ประเภท คือ
A. Free หรือ Naked nerve endings รับความรู้สึกเจ็บอุณหภูมิเย็น - ร้อน พบปลายประสาทสิ้นสุดตรงบริเวณรอบเซลล์หนังกำพร้าของผิวหนังถ้าพบรอบต่อมขน เรียก peritrichial endings
B. Encapsulated nerve endings บริเวณปลายประสาทมีเนื้อประสานหุ้มได้แก่1. Meissner's corpuscle (Figure168) รับความรู้สึกสัมผัส (light touch)
2. Pacinian corpuscle (Figure169)รับ pressure sensation
3. Ruffini corpuscle เป็น mechanoreceptors
4. Neuromuscular spindle (Figure170) รับความรู้สึกเกี่ยวกับ proprio-reception


