 |
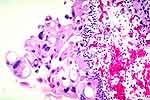
Figure 1: Thiotepa effects: pleomorphic nuclei,
abundant cytoplasm and vacuolar degeneration. |
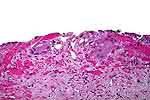 |
Figure 2: Shows Thiotepa effects on von Brunn
nests. |
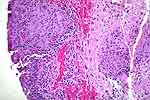 |
Figure 3: Two granulomas resulting from BCG
treatment (circles). |
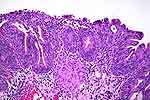 |
Figure 4: Shows one granuloma (circle) and
proliferative cystitis. |
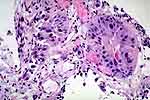 |
Figure 5: Radiation effect. The celluar changes
are similar to those seen with Thiotepa. |
 |
Figure 6: Radiation effect resulting in bizarre
nuclei. The nuclei have a smudged, degenerative apprearance but
distinction from pagetoid CIS could be difficult without a proven history
of radiation therapy. |

