|
1. |
This
is a simple epithelium. |
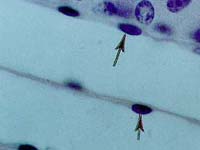 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
| 2. | In a pseudostratified epithelium, ……………………………………………. | 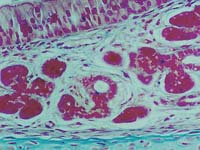 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
| 3. | If a membrane-impermeant fluorescent dye (MW <1,000) was injected into a single epithelial cell in the epidermis of the skin, you would expect it to appear in an adjacent epithelial cell due to …………………………………... | 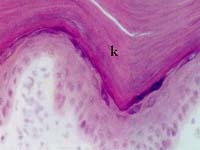 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
| 4. | Which epithelium (as seen in the photograph) can be distended to an extreme degree without losing its barrier function? | 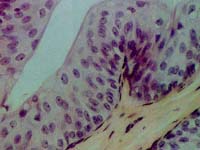 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
| 5. | Classify the epithelium that a physician first sees when examining a patient. | ||||||||||||||||||
|
| 6. | Goblet cells are classified as ….……………… . | 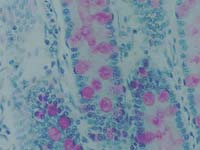 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
| 7. | Mixed exo-endocrine gland as seen in the photograph is | 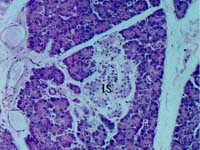 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
| 8. | The serous demilunes are mostly found in the parenchyma of ………………………. . | 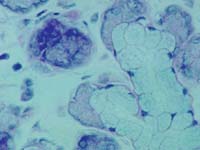 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
| 9. | The type of epithelium (as shown) is found in lining of ........... | 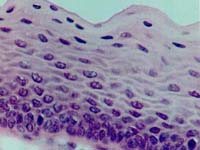 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
| 10. | The type of epithelium as seen in the screen, is ...................... epithelium ? |  |
|||||||||||||||||
|
| 11. | The basement membrane (BM) ………………………………… . | 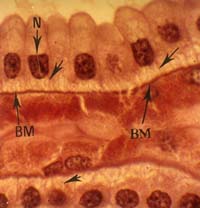 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
| 12. | All of the followings are true for the apocrine sweat glands, except | ||||||||||||||||||
|