Sporadic Translocation
Occurs when part of chromosome 21 breaks off during cell division and attaches to another chromosome, at or prior to conception.
Recurrence risk is low.
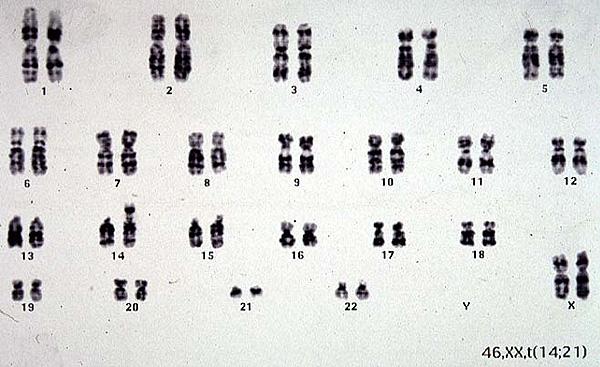
Down Syndrome caused by unbalanced translocation between chromosome 14 and 21
which results in 3 copies of chromosome 21.
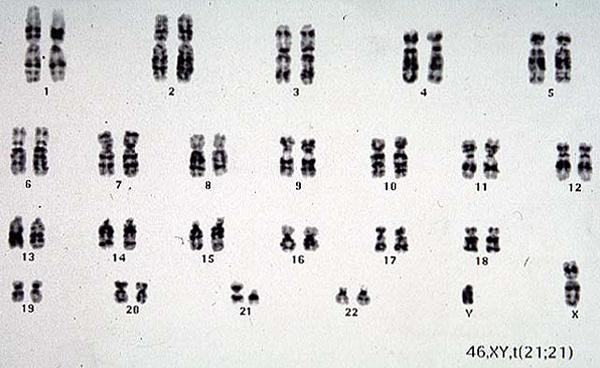
Down Syndrome caused by unbalanced translocation between chromosome 21 and 21
which results in 3 copies of chromosome 21.
Familial
Translocation
One parent is a balanced translocation carrier.
Recurrence risk depends on parental origin and number of chromosome involves.
Recurrence risk
| Type of translocation |
Parental origin |
Risk to offspring (%) |
| 13/21, 14/21,
15/21 |
mother
father |
10-15
3-5 |
| 21/22 |
mother
father |
10
2 |
| 21/21
|
mother
father |
100
100 |
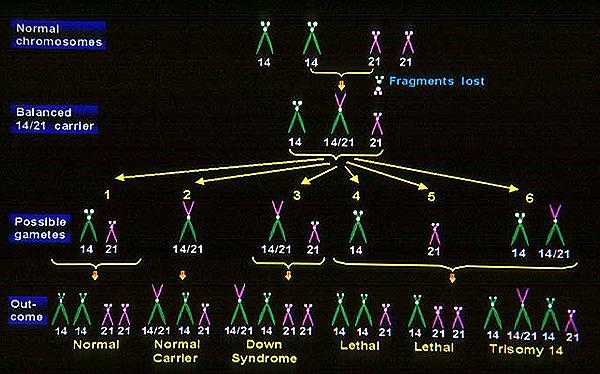
The picture shows gametes of a balanced translocation (14;21) carrier in one of the parent.
When unbalanced gamete fertilizes with a normal gamete will result in unbalanced embryos
with 3 copies of chromosome 21. (Down syndrome, translocation type)
Balanced translocation carrier
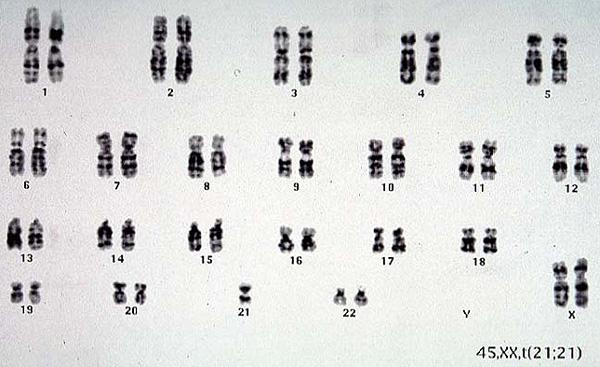
Balanced translocation carrier between chromosome 21 and 21 in female.
The phenotype is normal.
Karyotype 45, XX, t (21;21)
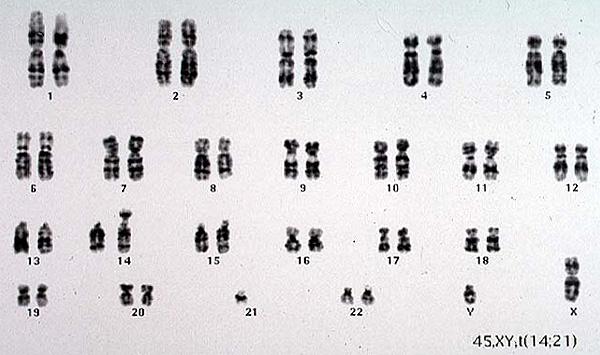
Balanced translocation carrier between chromosome 14 and 21 in male.
The phenotype is normal.
Karyotype 45, XY, t (14;21)
|




